Hello World! in C++
-
Ensure you have a working version of MediaPipe. See installation instructions.
-
To run the
hello worldexample:$ git clone https://github.com/google/mediapipe.git $ cd mediapipe $ export GLOG_logtostderr=1 # Need bazel flag 'MEDIAPIPE_DISABLE_GPU=1' as desktop GPU is not supported currently. $ bazel run --define MEDIAPIPE_DISABLE_GPU=1 \ mediapipe/examples/desktop/hello_world:hello_world # It should print 10 rows of Hello World! # Hello World! # Hello World! # Hello World! # Hello World! # Hello World! # Hello World! # Hello World! # Hello World! # Hello World! # Hello World! -
The
hello worldexample uses a simple MediaPipe graph in thePrintHelloWorld()function, defined in aCalculatorGraphConfigproto.absl::Status PrintHelloWorld() { // Configures a simple graph, which concatenates 2 PassThroughCalculators. CalculatorGraphConfig config = ParseTextProtoOrDie<CalculatorGraphConfig>(R"( input_stream: "in" output_stream: "out" node { calculator: "PassThroughCalculator" input_stream: "in" output_stream: "out1" } node { calculator: "PassThroughCalculator" input_stream: "out1" output_stream: "out" } )");You can visualize this graph using MediaPipe Visualizer by pasting the CalculatorGraphConfig content below into the visualizer. See here for help on the visualizer.
input_stream: "in" output_stream: "out" node { calculator: "PassThroughCalculator" input_stream: "in" output_stream: "out1" } node { calculator: "PassThroughCalculator" input_stream: "out1" output_stream: "out" }This graph consists of 1 graph input stream (
in) and 1 graph output stream (out), and 2PassThroughCalculators connected serially.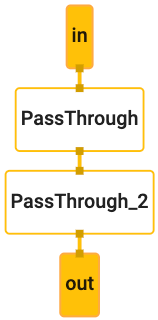
-
Before running the graph, an
OutputStreamPollerobject is connected to the output stream in order to later retrieve the graph output, and a graph run is started withStartRun.CalculatorGraph graph; MP_RETURN_IF_ERROR(graph.Initialize(config)); MP_ASSIGN_OR_RETURN(OutputStreamPoller poller, graph.AddOutputStreamPoller("out")); MP_RETURN_IF_ERROR(graph.StartRun({})); -
The example then creates 10 packets (each packet contains a string “Hello World!” with Timestamp values ranging from 0, 1, … 9) using the
MakePacketfunction, adds each packet into the graph through theininput stream, and finally closes the input stream to finish the graph run.for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) { MP_RETURN_IF_ERROR(graph.AddPacketToInputStream("in", MakePacket<std::string>("Hello World!").At(Timestamp(i)))); } MP_RETURN_IF_ERROR(graph.CloseInputStream("in")); -
Through the
OutputStreamPollerobject the example then retrieves all 10 packets from the output stream, gets the string content out of each packet and prints it to the output log.mediapipe::Packet packet; while (poller.Next(&packet)) { LOG(INFO) << packet.Get<string>(); }